Although still uncommon in Poland, this technology is gaining recognition across Europe and worldwide. Why is it worth paying attention to this trend? What benefits does floating solar bring? And how exactly does a floating solar farm work compared to traditional land-based farms?
Why Floating Solar?
Many countries face a shortage of space for new land-based PV installations, especially in densely populated areas. On top of this, there is increasing competition for land between agriculture, industry, and property development. Italy, for example, has prohibited further PV installations on agricultural land. New large-scale solar farms on inexpensive but ecologically valuable areas are raising concerns about biodiversity.
In Europe, this issue is particularly significant because many renewable energy installations are located in protected areas. This is why the European Commission is exploring and promoting innovations that minimize harm to ecosystems. In response to these challenges, floating solar farms are gaining momentum, offering renewable energy without the need for additional land. Solar installations on lakes and other bodies of water represent a step toward a sustainable future.
Floating solar panels
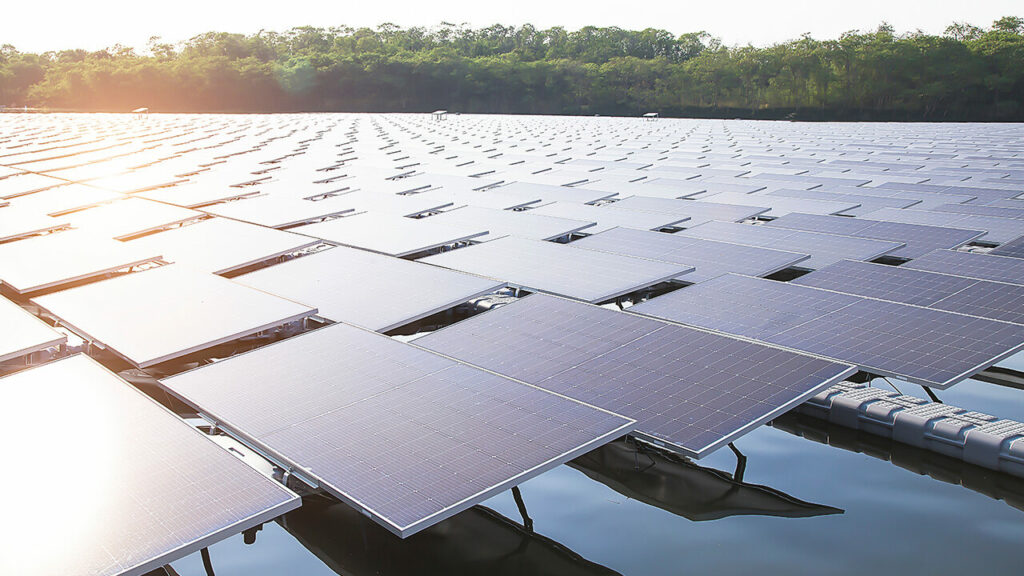

Floating solar farms rely on photovoltaic modules installed on special platforms that float on the surface of water bodies, such as lakes, irrigation ponds, reservoirs, or disused areas like decommissioned gravel pits. The goal is to utilize water bodies that aren’t used for tourism, sailing, agriculture, or other purposes.
Floating solar panels operate on the same principle as land-based photovoltaic systems, converting sunlight into electricity — direct current (DC) is transformed into alternating current (AC) through inverters. So, is this different from conventional PV installations? Not in the mechanism of energy production.
The floating platforms, made from buoyant materials, provide stability for the panels on water, while specialized anchoring systems keep them in place, preventing movement due to wind or water currents. The structure maintains flexibility, allowing the panels to adapt to water movements.
Using the water’s surface enables natural cooling of the panels, resulting in higher efficiency compared to ground-mounted installations.
Also read: What are PV panels? Discover your own energy from sunlight
When Did Floating Solar Farms Start Operating?
The history of floating solar panels dates back to 2007, when the first floating installation with a capacity of 20 kW was launched in Japan. This project laid the groundwork for the development of this technology in other countries, such as South Korea, China, and the United States. The growth of floating farms accelerated as it became clear that they could address land scarcity issues and improve energy production efficiency. Through collaboration among governments, industry, and research institutions, FPV system designs and efficiencies were refined.
Today, floating solar projects are emerging worldwide. In Europe, a floating solar farm with a capacity of 74.3 MW has been announced, to be built on an artificial reservoir at a former gravel pit in northeastern France.
In Poland, this technology is in the early stages of development. The first floating farm began operation in 2022 in Gdańsk, consisting of 110 panels with a capacity of 49.5 kWp installed on an artificial stormwater retention reservoir.
Advantages of Floating Solar Installations
In addition to generating clean energy and contributing to our energy system, helping advance renewable energy sources (RES) and the green revolution, floating solar farms offer several key benefits. To start, with the ability to save land and increase efficiency, floating solar are becoming increasingly popular in densely populated countries.
1. Optimal Use of Space
A floating solar power plant enhances our ability to utilize available space, especially in areas where land is scarce, too expensive, or highly productive (high-quality soils ensuring abundant yields). This is well illustrated by examples from Asian countries like Japan and South Korea. Floating photovoltaic technology also addresses land-use conflicts with the agricultural sector, which increasingly views large ground-mounted solar farms as a threat to diminishing farmland resources.
2. Better Lifespan and Efficiency of Panels
Floating solar panels achieve higher efficiency than ground-mounted systems, as water acts as a natural cooling system, preventing overheating. Utilizing water surfaces can increase the energy efficiency of the panels by up to 15%. Additionally, water reflects sunlight, which in normal conditions might be scattered or absorbed by the ground. The reflected light hits the panels again, boosting the amount of energy the panels can generate.
3. Easier Maintenance of Installations
Floating installations on water require less frequent cleaning. The air above water bodies contains fewer dust particles and pollutants compared to land areas, with water acting as a natural filter. In land-based systems, dirt reduces panel efficiency, necessitating regular cleaning. Additionally, vegetation often grows around ground-mounted installations, requiring frequent mowing – this is not an issue for floating installations.
Also read: PV panel maintenance: The key to extended life and efficiency
4. Water Environment Control
Can floating solar panels have a positive impact on water environment management? The partial shading of a water body by the panels limits algae growth, which can negatively affect water quality, especially in warmer climates. The reduction of sunlight reaching the water lowers its temperature, which can improve conditions for certain aquatic species. Additionally, floating solar farms can act as a wind barrier, reducing surface water wave action and helping protect the reservoir’s banks from erosion.
In the case of larger FPV projects, floating solar panels can help conserve water by preventing evaporation, which is particularly important in light of growing drought issues in many regions of the world.
Floating solar may also provide a solution for businesses that only have access to “water-based” areas, such as water reservoirs and basins at wastewater treatment plants, which store water for domestic and commercial use.
Also read: Industrial solar power – How to get started?
Floating PV system design
Floating PV projects require careful planning and analysis to maximize the use of floating technology and avoid issues related to water quality and the environment. Key steps include selecting an appropriate location that takes into account hydrological conditions and climate, as well as designing a structure that will perform well in aquatic conditions.
At Electrum, we design and build solar farms. Learn more from the article:
Solar Power System Design – What You Need to Know?
How does the design of floating PV installations look in Poland at the moment?
An important aspect here is the uncertainty regarding administrative decisions, such as the requirements under the Environmental Conditions Decision. Potential restrictions related to the impact of the installation on aquatic ecosystems must be considered, along with an analysis of how FPV projects will be classified under Polish regulations in terms of obtaining a Building Permit. Another key factor will be the possibility of securing the implementation of FPV in Local Spatial Development Plans and Protection Plans. Regarding the use of water for energy purposes, obtaining a water law permit will be necessary.
An important part of the project is also integration with the local energy grid and minimizing the impact of the installation on the ecosystem, for example, by monitoring the oxygen levels in the water and the quality of the aquatic environment.
Also read: Solar Interconnection | Grid connection requirements
In Electrum, we assist in defining an individual path to renewable energy sources, offering comprehensive support in designing and implementing photovoltaic technologies, including modern FPV systems.
Floating solar panels location
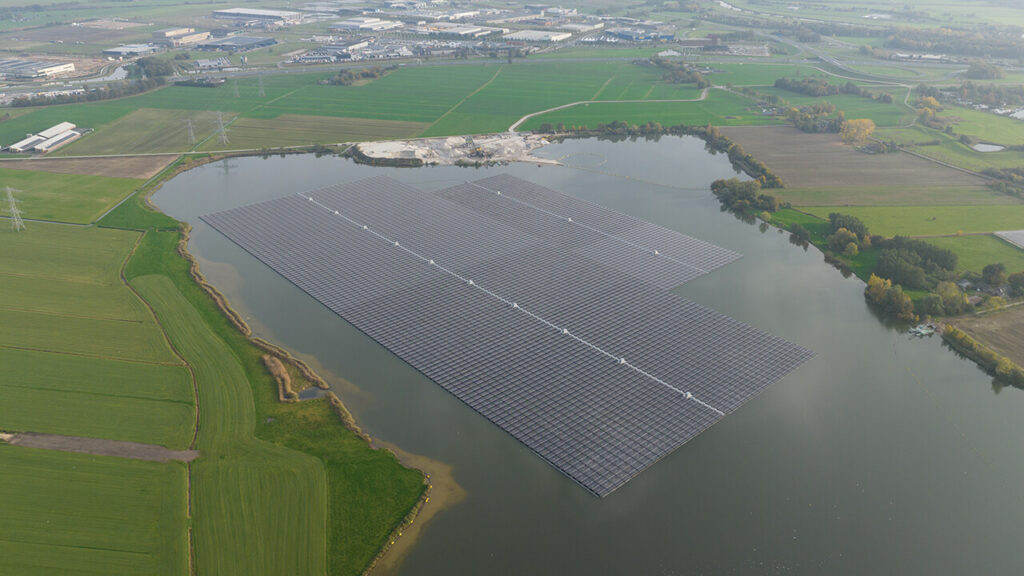

Placing floating solar panels on water primarily requires the selection of an appropriate water body – artificial lakes, reservoirs, or areas used for industrial purposes, such as wastewater treatment plants, are preferred. It is important that the water body has a stable water level and is not exposed to extreme weather conditions, such as strong currents or waves, which could damage the panels or reduce their efficiency.
In Poland, a significant factor affecting floating solar farms will be the changing seasons, especially winter and freezing temperatures, which may negatively impact the durability of the installation. To address this, durable materials resistant to low temperatures are used, along with flexible anchoring systems that allow the structures to adapt to ice movements. Some installations may also use heating systems to prevent the water around the panels from freezing. Alternatively, placing farms in deeper water bodies or limiting their operation to warmer months can reduce the risk of damage.
Floating solar farms and Costs
Floating solar panels are, of course, not without their challenges. A floating installation can cost 25% more than land-based systems. The panels carry the risk of lowering oxygen levels in the water, which can harm fish, and if the technology is not properly designed, the panels themselves can negatively impact water quality.
Although floating solar farms are more expensive than land-based systems, increasing financial support from the European Union for innovative energy technologies may help offset these cost differences. Poland has access to funds allocated for the development of renewable energy sources, which can support pilot floating photovoltaic (FPV) projects. Offered loans and grants can provide significant support to companies planning investments in floating PV farms. In Poland, the use of floating photovoltaic systems can contribute to sustainable energy development by reducing pressure on agricultural land and protected natural areas.
Read also: Solar farm construction: How We Do It at Electrum

Floating Solar Power Plants in Poland
In summary, a floating photovoltaic power plant, known as a floating PV system, is an innovative solution that allows for the production of clean energy without occupying valuable land.
These installations are placed on water bodies (solar panels are mounted on floating platforms), which not only saves space but also increases the efficiency of the panels by naturally cooling them with water.
Floating solar power plants are an ideal solution for areas with limited land space, and they also help reduce water evaporation.
We hope that the development of floating power plants in Poland is just a matter of time – floating farm projects are still in the conceptual phase, but initial analyses regarding their implementation are already emerging. Unfortunately, as with other renewable technologies such as offshore wind, green hydrogen, or energy storage, the implementation of FPV technology in Poland faces legislative hurdles. While the technology and potential are present, there is a lack of appropriate regulations that could speed up the adoption of this solution.
Polish companies are not yet widely engaged in the development of this technology. Electrum has considered the potential of floating PV, but, similar to agrivoltaics, legal barriers and the lack of legislative incentives hinder progress in this field.
A positive aspect is that the documented, long-term experience of other countries in this area will be helpful when we decide to introduce this technology on a larger scale. We have the opportunity to adapt the best practices and technologies to local conditions.
Floating PV – Summary
Finally, it is worth emphasizing that 70% of the Earth’s surface is covered by water. In the future, the use of floating photovoltaics may be expanded to ocean platforms, which would open new opportunities for harnessing energy from renewable sources. Ongoing research into structures capable of withstanding harsh marine conditions will create new possibilities for utilizing water surfaces.






